Does Website Structure Affect SEO?

You Bet Your Search Ranking It Does!
Despite the massive growth of social media, ranking on the top of search engine results is still extremely relevant for virtually every industry – including the financial industry. It is estimated that 71% of consumers use a search engine when considering a purchase.
With more than 75% of users clicking on first page search results it is no wonder SEO is so competitive! In search engines such as Google and Bing, if you don’t appear on the first page of results, it is almost as if you don’t exist. So, do everything you can to rank well and be found.
According to Google, content and backlinks (links pointing to your site) are the most important factors in SEO ranking, but keep in mind that focusing only on these two and turning a blind eye to other factors such as website structure will leave you in the dark in terms of search results.
Optimizing site structure is all about making life easier for search engines (and users) to navigate your site and find exactly what they are looking for. Google and other search engines uses bots, also called “spiders” or “crawlers”, to crawl your website. They figure out what your content is about, so they can define under what keyword searches your content should rank.
Here, we examine key aspects of getting your website structure fully optimized for SEO, so that your content gets seen.
Use Header 1 and Header 2 Tags
H1 tags tell search engines what is the headline of a specific page and H2 tags are the pages´s subheadings. Think of H1 tags as the title of a book and H2 tags as the chapters. In this article, “Does Website Structure Affect SEO?” is the only H1, and “You Bet Your Search Rankings!” is an example of one of the 7 subheadings in the page.
This is how it would look translated to HTML:
This article´s H1 tag would appear in the code as <h1>Does Website Structure Affect SEO?</h1>
This article´s H2 tag would appear in the code as <h2>You Bet Your Search Rankings!</h2>
H1 and H2 tags are important because they tell crawlers: “This is what you will find in this page, and this is what its about”, then, crawlers determine if it is relevant to show your page on a particular search result.
H1 and H2 Tag Tips:
- There is no need to use more than one H1 tag per page (in the same way as a page needs only one title).
- Don’t try to fool search engines. Make sure the H1 and H2 tags reflect exactly what is written in the page, if not, your page will be penalized and you will most likely rank lower.
H1 tags should not be confused with title tags which are used to specify the clickable headline of the page to be displayed in search engine results and social sharing.
Make Your Website Easy to Crawl and Index
A city needs to have streets that connect to every other street, so imagine what would happen to traffic if some streets were impassable? Total chaos. The same applies to your website. So make sure there are no dead ends in your structure.
Every page should take you to another page, internal links must connect one part of the website to another, and every page must display content that makes sense and serves the general purpose of your website. Dead ends make it difficult for crawlers to assess your content, and your website could end up getting booted out of Google’s search results.
Aside from maintaining a clean structure there are some very specific actions you can take to improve the crawlability if your website:
- First, your website needs to be indexed in Google. Getting your website indexed is as easy as submitting it here. Indexing tells Google about the existence of your website.
- Submitting a XML sitemap provides search engines with a list of all the pages your site contains, so that crawlers do not miss anything.
Although these steps do not guarantee that your website will be shown in search engines, it greatly increases the likelihood.
Use Internal Website Links to Your Advantage
Your users should be able to get from one page to another with ease. If your website is large and has many pages, you need to make sure all pages are accessible with only a few clicks. A good guideline is that a user should be able to reach any page in your website within 3 clicks.
Internal linking works by using keywords within your content and linking these keywords to other relevant pieces of content within your website.
Follow an Intuitive Hierarchy
The structure of your site should emulate a pyramid. On the top is your homepage, and underneath the homepage are your category and subcategory pages that lead to the content-centered pages. Usually, the pages below under the categories will be the ones vying for a position in search engines.
The trio category/subcategory/page structure is common for simple websites, but serves as a good starting point for much more complex sites like Amazon or Wikipedia.
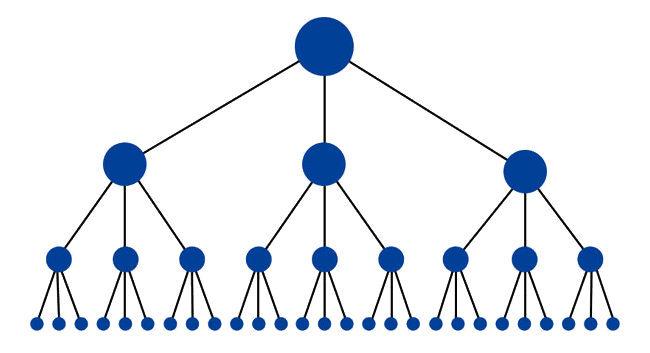
Example of a hierarchical layout (image source: http://moz.com/learn/seo/internal-link)
If possible, map out the structure of your website. A well-organized site often boosts pages-per-visit; Increasing the number of pages per visit correlates with positive Google search rankings.
Beware of Duplicate Website Pages
Google reads duplicate pages as spam! Since multiple versions of the same content (page) will not show in search results, Google is forced to choose which version to show, this confusion dilutes the visibility for each duplicate. Leverage web tools such as the Google Search Console to help eliminate duplicate pages.
Properly Craft the URL Structure
Your URL structure should imitate your navigation hierarchy and shouldn’t be too long or complex. Here is an example of what should be the optimal structure of your URLs:
http://www.example.com/category-keyword/subcategory-keyword/primary-keyword.html
The URL is broken down into Category → Subcategory → Page. This is easy for crawlers to read, and easy for your users to navigate. It includes the target keywords which is good for ranking, it indicates what the destination page will be about, and it doesn’t have special characters such as !$@? which makes crawling more difficult.
TIP: In terms of URL structure is that the closer the keywords are to the root domain, the more SEO-friendly the URL will be.
Avoid Generic Titles: Use Specific Keywords
Using specific keywords that you’re targeting to get ranked in your post titles and URL structure is essential. Avoid using boring generic titles that won’t rank well…or even compel a reader to click the URL. You’ll be clearly telling both the search engine and the reader what your post is about.
For example, using a generic title like Daily Market Commentary in a blog post title
http://www.rootdomain.com/blog/Daily-Market-Commentary
will be less SEO-friendly (and less reader-friendly) than using a specific keyword-rich title, such as Market Trends Influencing Soybean Futures Prices
http://www.rootdomain.com/blog/Market-Trends-Influencing-Soybean-Futures-Prices
It Pays to Pay Attention to Detail
While search engines place emphasis on content and backlinks in determining SEO, they also consider several aspects of a website to determine how SEO worthy it is – judging everything from design to usability – and the structural basics of a website play a key role in search ranking.
It pays to pay attention to the details of your website structure – so your business can maintain a competitive edge in ranking well in online search. Proper usage of website header tags, indexing, cross-linking, hierarchy, URL structure, and keywords are just a few elements that should be given special attention to ensure that your website is optimized for search.
__
Interested in learning more about SEO or website optimization? Contact Gate 39 Media
Editor’s Picks
Many people are skeptical or even afraid of Artificial Intelligence (AI). But we've been using it to enhance our team and capabilities. The real...


Connect with us to discover how we can help your business grow.
.jpg)
